Now Reading: Periyar Tiger Reserve Confirms 12 New Faunal Species
-
01
Periyar Tiger Reserve Confirms 12 New Faunal Species
Periyar Tiger Reserve Confirms 12 New Faunal Species

swift Summary
- A biodiversity survey at the Periyar Tiger Reserve (PTR) conducted from September 11 to 14 added 12 new species records to its faunal checklist, including eight butterflies, two odonates (dragonflies/damselflies), and two subspecies of birds.
- Organised by PTR in collaboration with the Kerala Forest Department, Periyar Tiger Conservation Foundation, and Travancore Nature History Society, teams were deployed across 26 basecamps within PTR’s expansive 925-sq.km area in Idukki and Pathanamthitta districts.
- Key findings:
– Butterflies: Eight new species recorded (e.g., Sahyadri Grass yellow, Plain Orange-tip).
– Odonates: Two new additions (Sahyadri Torrent-Hawk and Coorg Torrent-Hawk).
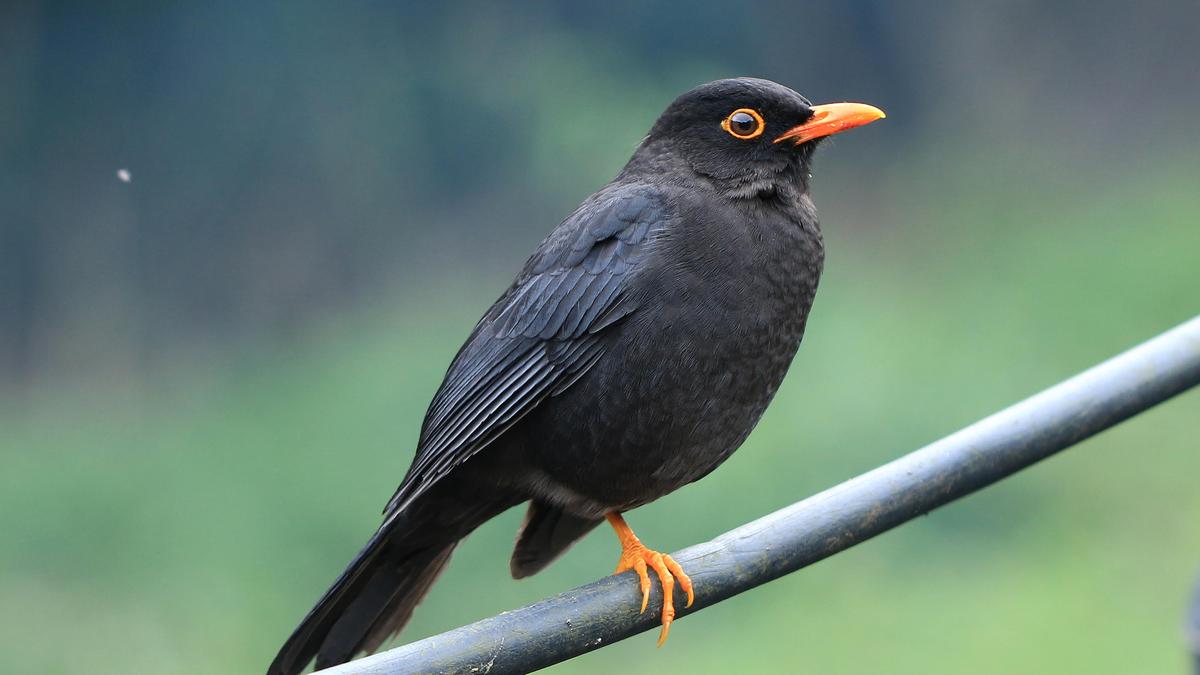
– Birds: Subspecies like Bourdillon’s Blackbird and White-throated Ground Thrush confirmed; notable sightings include Great Indian Hornbill, Nilgiri Wood Pigeon, etc.
– Other fauna observed includes Bengal tigers, elephants, mongoose species, otters, civets, porcupines.
- PTR now boasts over 300 bird species and supports megafauna such as tigers and elephants alongside endemic flora/fauna indicative of its montane shola forest habitat diversity.
Indian opinion analysis
the addition of twelve faunal species to the biodiversity roster underscores Periyar Tiger Reserve’s meaning as a critical ecological hotspot in India’s Western Ghats. Such surveys not only enrich scientific knowledge but also highlight the region’s fragility amidst growing environmental concerns.
Collaboration between government agencies and research organisations provides a robust model for conservation monitoring that could be replicated nationally. The presence of rare endemics-such as these newly documented odonates or butterflies-positions PTR not just as a “living laboratory” but also as an emblem for global conservation priorities tied to UNESCO World Heritage sites like the Western Ghats.
Moreover, identifying lesser-known taxa strengthens arguments against intrusive development projects threatening such ecosystems while advancing India’s standing in international environmental stewardship efforts.Continued investments in biodiversity studies would likely enable further discoveries critical for policymaking around climate resilience.
For more detailed data on this story: Read More