Now Reading: Early Humans Walked 8 Miles to Source Ideal Stone Tools
-
01
Early Humans Walked 8 Miles to Source Ideal Stone Tools
Early Humans Walked 8 Miles to Source Ideal Stone Tools

Fast Summary:
- Around 2.6 million years ago, early hominins in Nyayanga, Kenya, began traveling long distances (over 8 miles) to source high-quality rocks for tool-making.
- These tools, known as Oldowan tools, were standardized and deliberately crafted for tasks like cutting plants and butchering meat.
- A recent study published in Science Advances suggests this refined behaviour occurred 600,000 years earlier than previously thought.
- Analysis of artifacts at Nyayanga indicates that rocks were transported from far away because local stones were too soft.
- Evidence challenges the notion that such long-distance stone procurement first happened around 2 million years ago in Kanjera, Kenya.
- This behavior highlights early planning and forethought among hominins-parallels drawn with the foundations of food sharing within groups.
- Both Homo species and extinct hominin genus Paranthropus may have contributed to this innovation.
Image Details:
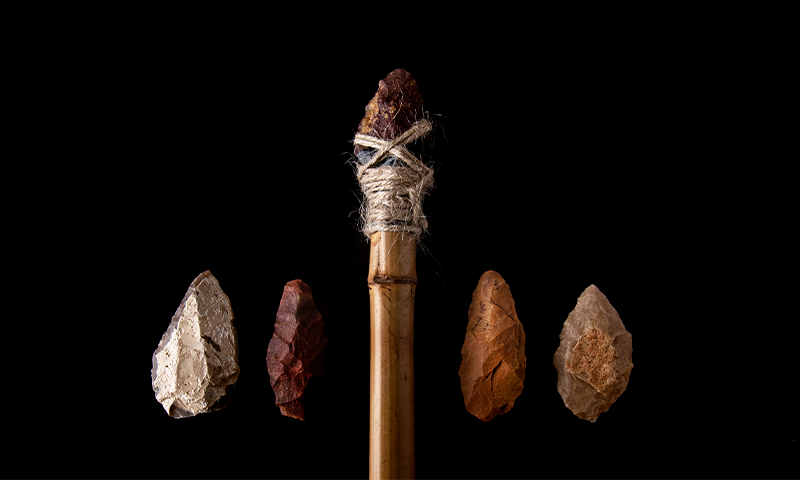
- Stone knife from over 2 million years ago showcasing a sharpened edge used for basic tasks.
Credit: Appio Studios / Shutterstock.
Indian Opinion Analysis:
This discovery deepens our understanding of human evolution by highlighting how advanced planning and collaboration existed much earlier than traditionally believed. The ability of early humans to walk considerable distances for resources points to a complex understanding of spatial habitat along with prioritization over immediate survival instincts-a foundational trait seen even today across human societies.
For India, these findings underline parallels in the importance given to resource acquisition across vast terrains-a practice evident in ancient civilizations like those living along the Indus Valley. As cultural tracing frequently enough aligns evolutionary behaviors with practical advancements like large-scale agriculture or trade systems seen historically across South Asia’s diverse geography-it reaffirms how essential resource optimization remains central to human progress. Moreover, India’s archaeological community could leverage similar methodologies when examining its own prehistoric sites.