Now Reading: Revolutionary Hot Glue Gun Tech Aims to Heal Broken Bones
-
01
Revolutionary Hot Glue Gun Tech Aims to Heal Broken Bones
Revolutionary Hot Glue Gun Tech Aims to Heal Broken Bones
Quick Summary
- Researchers have modified hot glue guns to repair damaged bones,offering a fast and cost-effective method during surgery.
- The modified glue gun operates at a reduced temperature of 60°C and uses a biodegradable material combining hydroxyapatite (found in human bones) and polycaprolactone.
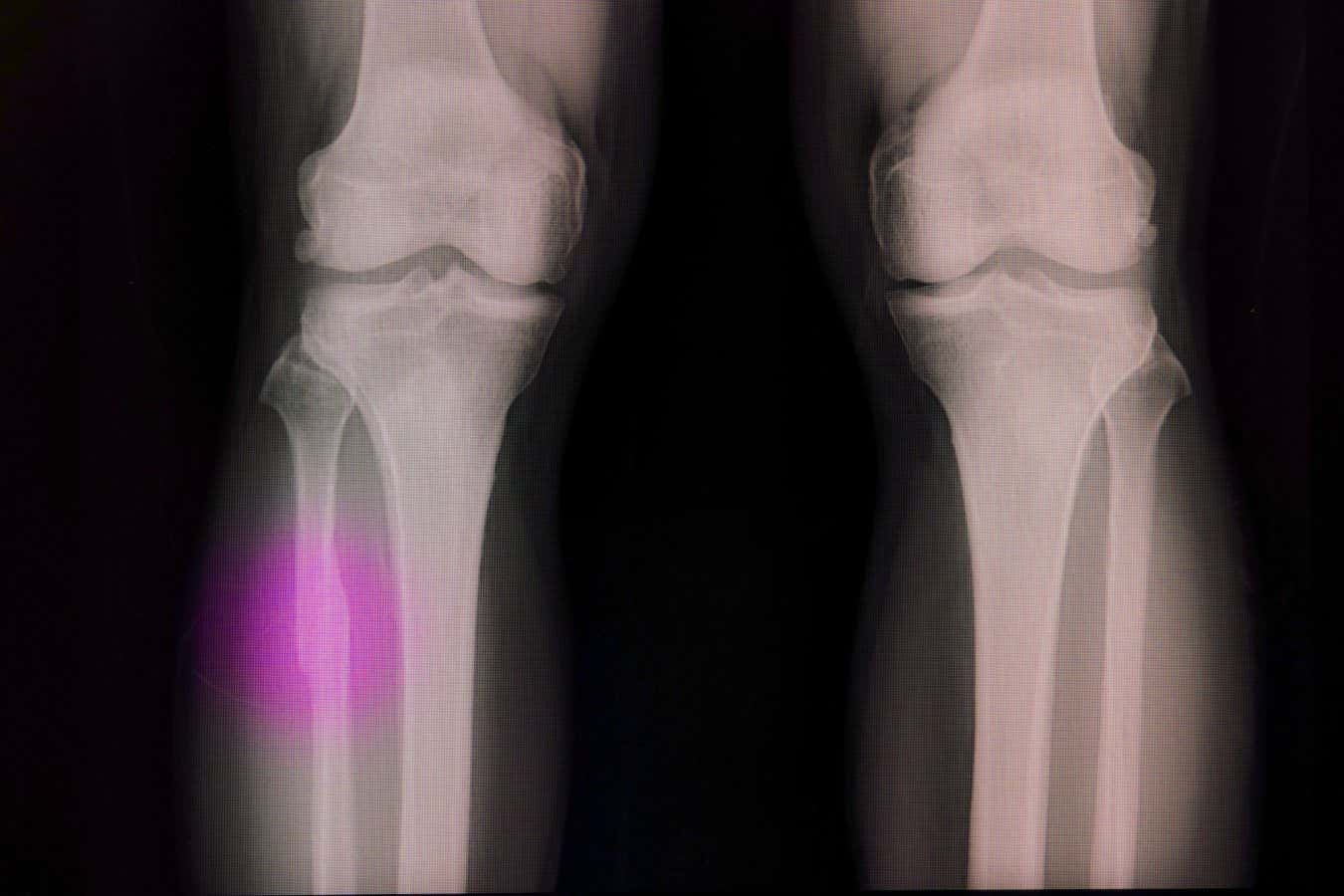
- This technique fills bone voids quickly during surgery, allowing natural bone cells to span the gap for permanent repair over time.
- Tested on rabbits’ femur bones, results showed no separation or medical issues after 12 weeks, with higher bone volume compared to traditional methods.
- Antibacterial drugs like vancomycin and gentamicin can also be included in the filament for gradual release at the surgical site, reducing infection risks.
- Some experts remain skeptical about its widespread adoption compared to advancements in 3D scanning and printing technologies.
Image Caption: “Broken bones frequently enough need a material to fill the void.”
Indian Opinion Analysis
The innovation of using a modified hot glue gun for repairing bone injuries could substantially benefit healthcare worldwide by reducing costs and treatment times-features particularly impactful for developing nations like India. Hospitals often face resource constraints,making this ready-to-use solution potentially more accessible than advanced technologies like 3D printing.
Nevertheless, global skepticism surrounding its long-term effectiveness may suggest limitations in adoption unless further extensive clinical trials are conducted on humans. For India specifically, if successfully proven safe and effective across diverse medical conditions, this technology provides an prospect to address trauma care disparities in rural areas where specialized equipment is limited.