Now Reading: SpaceX Dragon Capsule Successfully Raises ISS Orbit in Crucial Test
-
01
SpaceX Dragon Capsule Successfully Raises ISS Orbit in Crucial Test
SpaceX Dragon Capsule Successfully Raises ISS Orbit in Crucial Test

Swift Summary
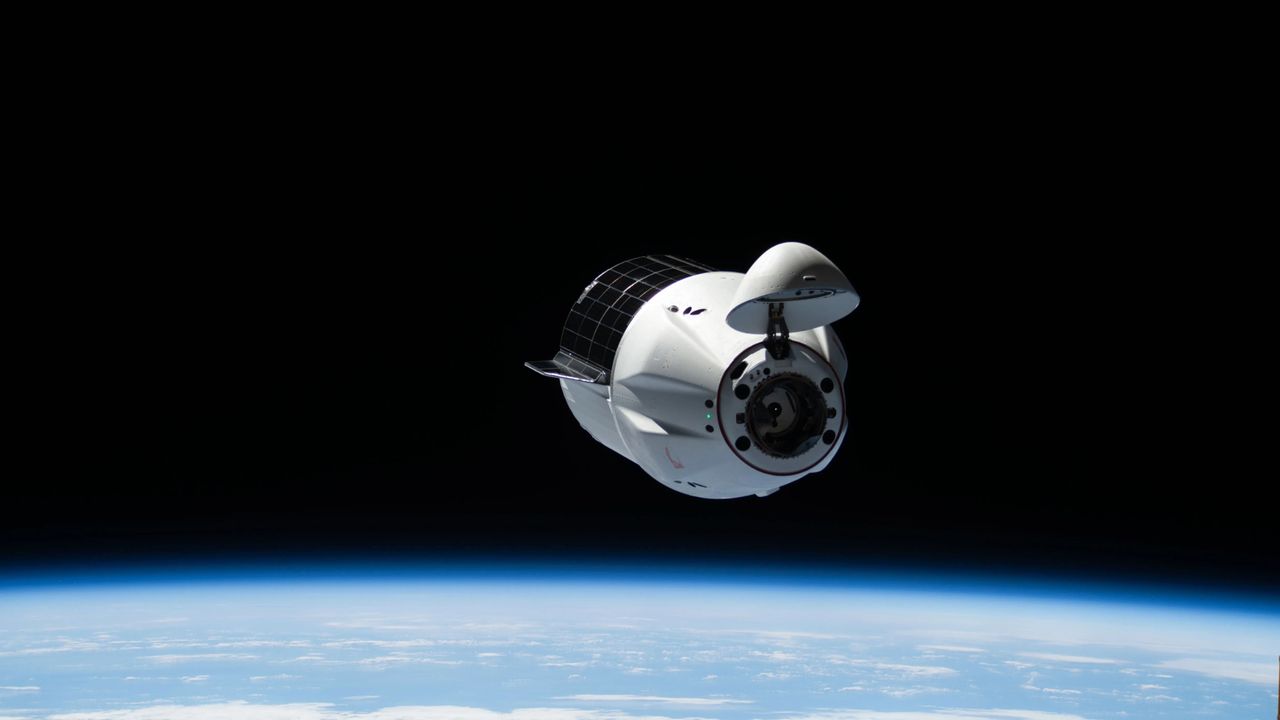
- SpaceX’s Dragon cargo spacecraft successfully boosted the International Space Station (ISS) higher in its orbit during a test maneuver on September 3, 2025.
- The maneuver involved firing two Draco engines for 5 minutes and 3 seconds, raising the station’s orbit to approximately 260.9 by 256.3 miles (419.9 by 412 km).
- Reboosting is necessary due to atmospheric drag that slowly pulls the ISS closer to Earth over time; it has historically been performed by Russian Progress spacecraft.
- With russia possibly exiting the ISS program in 2028, NASA is turning to U.S.-based resupply crafts like SpaceX’s Dragon and Northrop Grumman’s Cygnus for these operations.
- This test marked one of several boosts planned throughout fall 2025 using Dragon’s new boost kit technology.
- Such tests also prepare SpaceX for another critical task: deorbiting the ISS when its mission ends around late 2030 or early 2031 using a specialized “monster” Dragon capsule.
- The current Dragon capsule arrived at the ISS on august 25 during SpaceX’s CRS-33 mission,delivering supplies and scientific equipment weighing about 5,000 pounds (2,270 kilograms). It will return to Earth between December and January with discarded items from the station.
Indian Opinion Analysis
SpaceX’s successful reboost of the ISS signals growing efforts by NASA and commercial partners to ensure long-term operational sustainability as international dynamics around space collaboration shift. For India-a country advancing rapidly in space technology-such developments underline key lessons on technological self-reliance and cross-sector partnerships within space exploration systems.
The potential withdrawal of russian collaboration on key functions such as reboosts highlights vulnerabilities within international cooperative systems but also opens avenues for greater participation from emerging players like India in future global ventures post-ISS era.
India might observe how nations are integrating commercial entities into pivotal roles traditionally dominated by government space agencies-an approach that In-Space or ISRO could adapt strategically while fostering private sector innovation domestically.India remains neutral yet watchful toward developments of this scale as they may widen opportunities for deeper bilateral collaboration or create new competitive frameworks globally ahead of hypothetical post-ISS platforms like low-earth orbit stations.Read More