Now Reading: Tracking the Sun: Current Phase in Its 11-Year Solar Cycle
-
01
Tracking the Sun: Current Phase in Its 11-Year Solar Cycle
Tracking the Sun: Current Phase in Its 11-Year Solar Cycle
Rapid Summary:
- The sun operates on an 11-year solar cycle marked by periods of high (solar maximum) and low activity (solar minimum).
- These cycles are defined through sunspot observations, with peaks evaluated using a smoothed average over 13 months.
- Solar Cycle 25 began in December 2019, with predictions estimating its peak to be around August or September 2025.
- However, new data show the cycle outperforming earlier expectations, with the actual peak likely in October 2024.
- As October 2024, solar activity has begun declining, transitioning into the cycle’s downward phase where fewer sunspots are expected but large flares and CMEs remain possible.
- Recent sunspot regions triggered geomagnetic storms on sept. 1-2 via associated coronal mass ejections (CMEs).
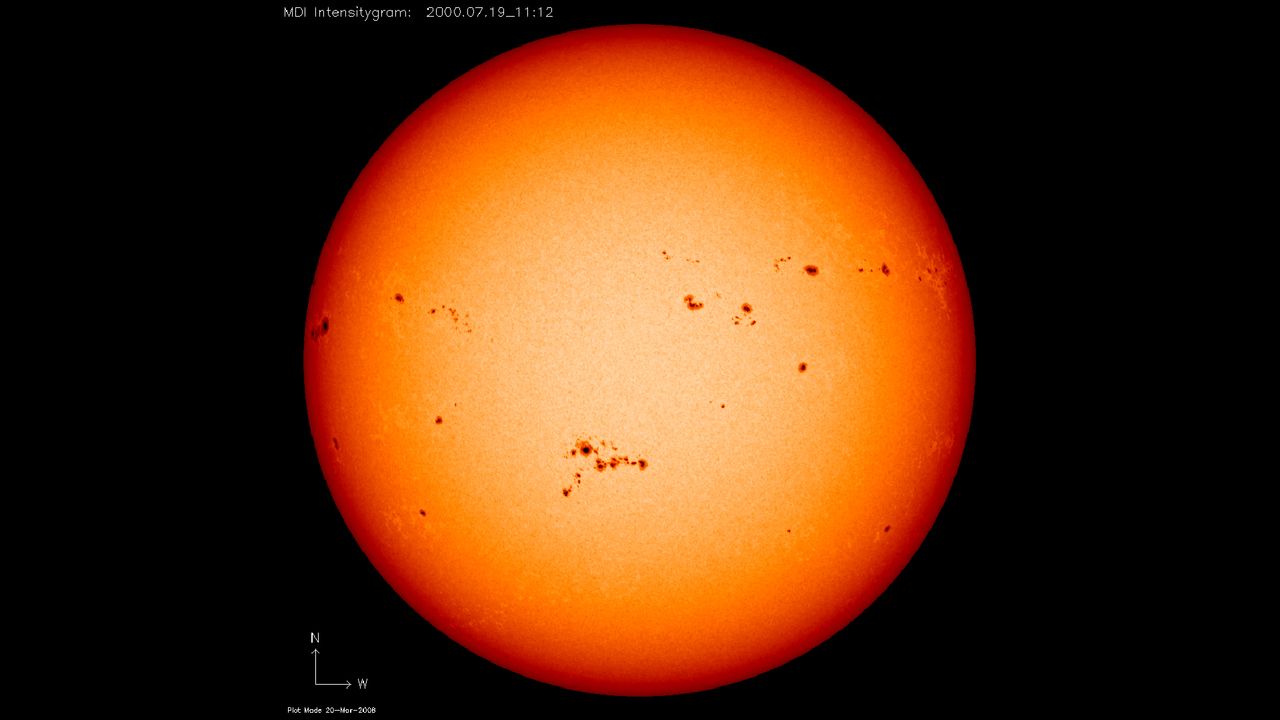
!The Sun’s spotty face photographed by NASA’s Solar and Heliospheric Observatory
Indian Opinion analysis:
Understanding the dynamics of solar cycles is notable globally, but particularly important for India as it continues its space exploration ambitions through missions like Aditya-L1 aimed at studying the Sun. India’s technological frameworks also rely heavily on satellites that are vulnerable to disruptions caused by intensified phenomena such as coronal mass ejections during active phases of these cycles.Given that India manages critical infrastructure through satellite communications and GPS services for agriculture, defense systems, aviation navigation control networks etc limits + resilient-solace priority future statistical average weeks존 safety before decoding real-msg-range againstdisplacement hacked faults