Now Reading: Webb Telescope Explores Atmosphere of TRAPPIST-1e in Habitable Zone
-
01
Webb Telescope Explores Atmosphere of TRAPPIST-1e in Habitable Zone
Webb Telescope Explores Atmosphere of TRAPPIST-1e in Habitable Zone
Swift Summary:
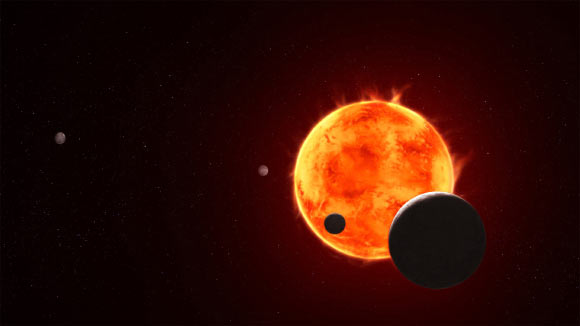
- Astronomers using the James Webb Space Telescope (NASA/ESA/CSA) are studying TRAPPIST-1e, one of seven Earth-sized exoplanets in the TRAPPIST-1 system located 38.8 light-years away in Aquarius.
- TRAPPIST-1 is an ultracool dwarf star that generates frequent UV radiation flares and has only 8% of the Sun’s mass.
- Webb’s observations analyzed starlight passing through potential atmospheres during transits of TRAPPIST-1e, collecting data on possible chemical makeup.
- Only four transits have been analyzed so far; an atmosphere has not been confirmed yet, but researchers suggest that any original hydrogen-helium atmosphere may have been stripped away by stellar radiation.
- The study indicates possibilities ranging from no secondary atmosphere to surface environments featuring a global ocean or methane-enriched conditions like Saturn’s moon Titan.
- Tidally locked planets like TRAPPIST-1e feature perpetual day and night sides; liquid water could exist in smaller areas due to greenhouse effects stabilizing temperatures with gases such as carbon dioxide.
- Researchers are exploring innovative methods for analyzing Webb data and warn against drawing direct parallels with Earth-like planetary systems due to key differences between TRAPPIST stars and our Sun.
Image included: Conceptual depiction of TRAPPIST-1e silhouetted against its flaring host star.
Indian Opinion Analysis:
The findings on exoplanetary atmospheres from the James Webb Telescope mark important progress toward understanding distant worlds possibly capable of harboring life. For India, where space programs like ISRO foster growing interest in astronomy and exploration, such advancements offer broader inspiration to intensify research collaborations with global missions focused on outer space discoveries.
TRAPPIST-type systems challenge existing scientific models because their unique environmental factors-such as tidal locking or high UV activity-defy conventional assumptions based on Earth’s conditions. From a strategic viewpoint, this underlines how international engagement in cutting-edge tools like telescopes provides nations an chance to contribute new insights while benefiting scientifically.
moreover, this research signifies how interdisciplinary approaches combining astronomy with climate modeling play critical roles when imagining choice ecosystems beyond Earth. As India advances indigenous technology for astrobiology or climate studies linked indirectly here by topics involving atmospheric stability/water zones-the findings reinforce India’s potential positioning toward leadership roles globally within fields these sciences intersect.